As data centers evolve to support new AI companies and AI-based applications, fiber optic connectivity has become crucial. Fiber optic cables are preferred in data centers due to their high bandwidth, long-distance transmission, low latency, and resistance to electromagnetic interference (EMI). These fast, reliable connections between data centers and cloud providers enable quick data transfers and low latency, which is essential for cloud-based applications.
Key Facts About Fiber Optics
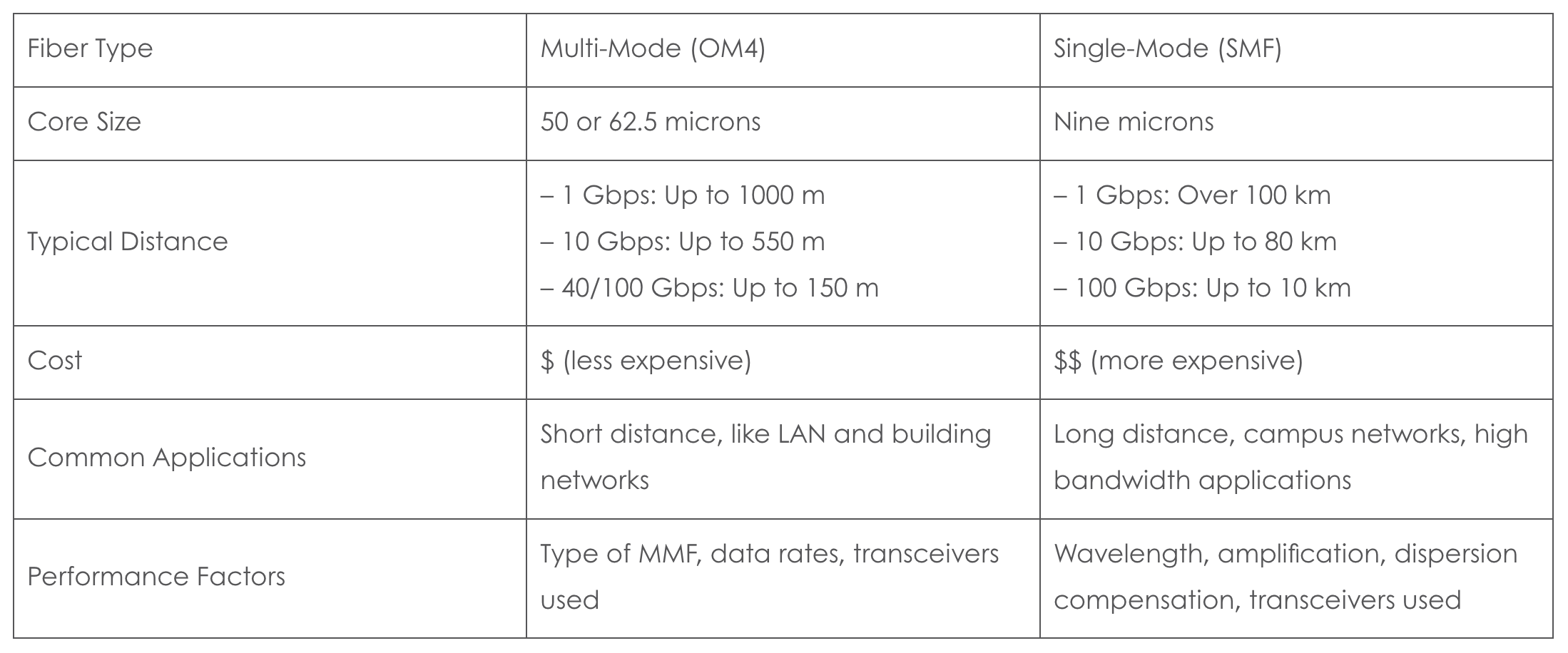
Fiber optic cables come in two main types: single-mode and multi-mode. Both types play vital roles in data centers.
Single-Mode Fiber (SMF) has a smaller core diameter (about nine microns) and is ideal for long-distance transmission with higher bandwidth.
Multi-Mode Fiber (MMF) has a larger core diameter (50 or 62.5 microns) and is used for shorter distances because it has higher attenuation (signal loss), and lower bandwidth compared to single-mode.
The transmission distance of MMF depends on several factors, including the type of MMF, the data rate, and the transceivers used. SMF, due to its smaller core and the use of laser light, can carry data over much longer distances.
While MMF is more affordable for short-distance applications, SMF, though costlier, is necessary for longer distances and higher speeds. SMF is often used in long-haul telecommunications, high-speed data centers, and campus-wide networks, whereas MMF is common in local area networks (LANs) and shorter, intra-building connections.
Fiber Types Comparison
Fiber Optics: A Green, Powerful Solution
As data centers pack in more equipment and power, energy efficiency becomes a priority. Fiber optics are more energy-efficient than other cable types due to lower signal loss and reduced reliance on repeaters. They also support virtualization and cloud computing, reducing the need for physical hardware. Additionally, fiber enables better cable management, which is crucial for cooling, one of the most energy-intensive operations in data centers.
Effective cable management improves airflow and reduces the need for excessive cooling, lowering power consumption. It also simplifies maintenance and troubleshooting, which cuts down on repair-related energy use and downtime.
Want to Learn More About Fiber Optics?
Check out the standards that govern fiber optic cabling in data centers. These standards ensure uniformity and compatibility in fiber optic infrastructure. Some key standards include:
TIA-942: Telecommunications Infrastructure Standard for Data Centers
ISO/IEC 24764: International Standard for Data Center Cabling
IEEE 802.3: Standards for Ethernet
Would you like to hear more?
Our experts would love to hear about your systems and how we can help

